Reliable electricity is important for daily life, but many households in states like Assam, Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha, and Uttar Pradesh still face power shortages. Off-grid solar systems offer a clean and dependable solution. By using solar energy, these systems can power lights, fans, and other essential appliances—even in remote areas.
Are you excited to include an off-grid solar system in your home, get freedom from power cuts, and bring light to even the most remote areas? Read Brick & Bolt‘s blog to understand more about off-grid solar systems for homes.
What Is an Off-Grid Solar System?
An off-grid solar PV system or off-grid solar system, is a solar power system unconnected to the utility electrical grid. Therefore, it is called a stand-alone power system (SAPS). The solar panels capture solar energy during the day, and the storage battery stores the extra energy to power electrical appliances at night. This system is used in areas where the utility grid doesn’t service (such as rural areas or islands). Off-grid systems offer electricity to these remote areas.
Your house can be more self-reliant with an off-grid solar system. But, off-grid systems are very expensive. You need to have a lot of battery storage to power a complete home without help from the grid, and the cost increases. When you go for the off-grid solar system, you need to monitor their consumption and solar production to ensure they have the required electricity.
Major Components of Off-Grid Solar System for Home
The key components of an off-grid solar system commonly involve solar panels, a storage battery, a charge controller, and an inverter.
Solar panels
Solar panels are an essential component of any solar power system. Off-grid solar panels collect sunlight and transform it into direct current electricity. In an off-grid system, this electricity is used directly or stored in batteries for later use. The solar panels give DC power.
Many types of solar panel installations exist, including ground-mounted and roof-mounted systems.
These mounted options depend on the available space, the exposure to sunlight, and personal preference.
- Roof-mounted systems are suitable for smaller properties with limited space like small houses or tiny houses.
- Ground-mounted systems work well for larger properties with ample space like bungalows and luxury kothis.
Solar Charge Controller
The charge controller is one of the major components of an off-grid solar system. It is used to regulate the electricity flow from solar panels to batteries, preventing overcharging by controlling the rate at which electric current is added to or drawn from the batteries. This will help extend the battery life and ensure the solar power system’s overall efficiency and safety.
Batteries
In a solar system, batteries store excess energy generated by the solar panels. This stored energy can be used during nighttime or when the sun isn’t shining to achieve a consistent power supply. The battery type and size depend on your energy requirements and consumption patterns. The selection depends on various factors, including cost, maintenance requirements, and lifespan.
Off-Grid Solar Inverter
The inverter is used to convert the battery’s stored DC power into alternating current (AC) power. It is accomplished by changing the electricity frequency and voltage, making it compatible with standard household outlets.
How Does an Off-Grid Solar System Work?
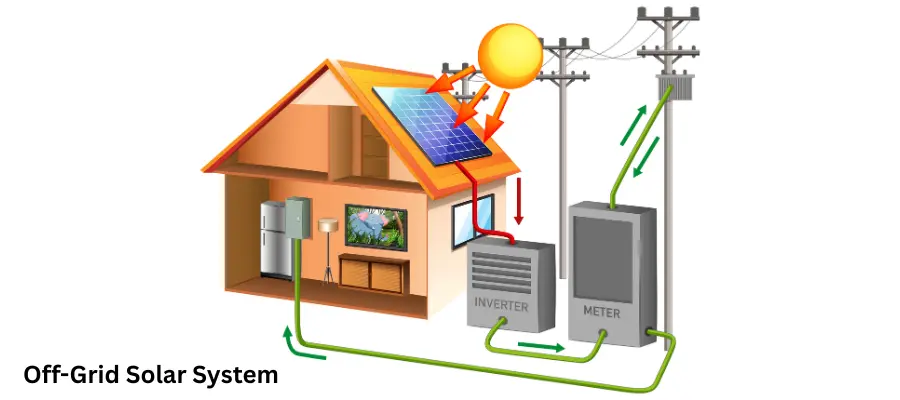
These systems enable users to generate, store, and use solar power independently, without depending on utility providers.
Here’s how an off-grid solar system works, step by step:
Step 1: Solar panels collect sunlight and convert it to DC electricity.
The process begins when solar panels absorb sunlight and generate direct current (DC) electricity.
Step 2: The charge controller regulates battery charging.
The DC electricity flows to a solar charge controller, which ensures the batteries are charged optimally and safely by preventing overcharging or deep discharging.
Step 3: Batteries store excess energy for later use.
During the day, any surplus electricity is stored in solar batteries. This stored power can be used at night or when sunlight is low.
Step 4: Inverter converts DC to AC for home appliances.
Finally, the inverter converts the stored DC electricity into alternating current (AC), the standard form of electricity most household and business appliances use.
Off-grid solar power systems are suitable for homes or buildings in remote areas where the main electricity grid is limited or unavailable. These stand-alone power systems help users save on electricity bills while promoting clean, renewable energy.
Interested in the broader benefits of renewable energy in construction? Discover how renewable energy is transforming construction projects.
Benefits of an Off-Grid Solar System
By installing off-grid solar systems, you can experience the following benefits:
No connection to the power grid: You generate your power through this solar PV system, which is very stable but dependent on the batteries and the bank’s sizes.
Self-reliance in terms of energy: The off-grid solar system is completely independent of electricity sellers. You won’t need to pay extra for electricity, and you’ll be completely safe from rising energy prices.
Outage Protection: The system also protects from grid-connected power outages or blackouts.
Reliability: Off-grid solar systems offer energy independence, which adds a layer of security and reliability. Since they operate independently from the utility grid, they are not affected by power outages, ensuring a continuous power supply even during grid failures.
Challenges & Considerations of an Off-Grid Solar System
- High Initial Cost: Compared to other types of solar systems, off-grid solar systems have a high initial cost. But in the long run, it will be cost-effective.
- Solar panel maintenance: You need to clean the solar panel regularly for better efficiency. It can be pricey based on the location.
- Battery maintenance: Periodically, you need to replace the old batteries at high prices. Traditional lead-acid batteries typically last 2 to 3 years and need to be replaced periodically, which can be costly over time. In contrast, lithium batteries have become a popular and more cost-effective choice in recent years (with a maximum 10-year lifespan).
- Nighttime and cloudy weather performance: Off-grid solar systems do not generate electricity at night and produce limited power during cloudy or rainy weather. To ensure a continuous power supply, especially during these periods, you’ll need to rely on a larger battery bank that can store enough energy during sunny days. In some cases, a backup generator is also recommended to support essential appliances when solar production is low or battery storage is depleted.
How to Size an Off-Grid Solar System for Your Home?
Calculate Daily Energy Consumption (kWh)
Start by identifying the power consumption of each device. Multiply the wattage by the number of hours used per day.
Example: A device uses 10 watts for 24 hours:
10 W × 24 hours = 240 watt-hours/day = 0.24 kWh/day
Determine Solar Panel and Battery Capacity Needed
To size your battery:
- Add 10% for inverter inefficiency → 240 Wh × 1.1 = 264 Wh
- Add 59% for cold temperature (20°F) → 264 Wh × 1.59 = 419.76 Wh
- Add 20% for battery charge/discharge inefficiency → 419.76 × 1.2 = 503.7 Wh/day
- For 5 days of autonomy: 503.7 × 5 = 2,518.5 Wh = 2.52 kWh
Battery capacity in ampere-hours (Ah):
- 2,518.5 Wh ÷ 12V = 210 Ah (rounded)
Factor in Location, Sunlight Hours, and Efficiency Losses
Assume 2.5 peak sun hours:
240 Wh ÷ 2.5 = 96 W minimum PV array
Add 15% loss: 96 ÷ 0.85 = 113 W solar panel
This ensures reliable power even during cloudy days or low sunlight.
Off-Grid Solar System Cost in India
Major factors influencing the off-grid solar power systems cost are the type and capacity of batteries (lead-acid vs. lithium), the overall system size, and installation complexity. Higher battery backup requirements and premium components can significantly increase the total expense.
The average price of an off-grid solar system in India typically ranges from ₹85,000 to ₹1,05,000 for a 1kW system, with the cost scaling up for larger capacities-reaching up to ₹7 lakh or more for a 10kW system, including installation and batteries.
For those aiming for maximum sustainability, explore net-zero energy buildings (NZEB) as the ultimate goal.
An off-grid solar system is best for remote homes, eco-conscious homeowners, and those seeking complete energy independence, as it provides reliable power without reliance on the utility grid. However, it requires a higher initial investment for batteries and equipment and careful energy management, and it is best when your location has limited or no grid access. Consider your budget, day-to-day energy requirements, and local sunlight availability before opting for the off-grid solar system.
Frequently Asked Questions
Off Grid vs On Grid Solar System: Which One is Better for You?
On-grid solar systems are ideal for homes in areas with reliable electricity since they are cost-effective and eligible for government subsidies, while off-grid systems suit remote locations or places with unreliable power, offering complete energy independence but at a higher cost due to batteries.
How Off-Grid Solar System Works?
An off-grid solar system generates electricity from solar panels, stores excess energy in batteries, and uses this stored power to run appliances even when the sun isn’t shining, making it fully independent from the main electricity grid.
Is an Off-Grid Solar System Right for Your Home?
An off-grid solar system is right for homes in remote or rural areas where grid access is limited or unreliable, or for those wanting full energy autonomy, despite higher installation and maintenance costs.
How to decide the appropriate size for an off-grid solar system?
- List all electrical appliances and calculate your total daily energy use in watt-hours (Wh) or kilowatt-hours (kWh).
- Find the average number of peak sunlight hours available in your area.
- Divide your total energy use by these sun hours to estimate the solar system size (in kW).
- Adjust for efficiency losses, battery backup needs, and future energy growth. Consult a solar expert for accurate sizing.
What are different factors to consider when choosing on-grid or off-grid solar systems?
Key factors include your area’s grid reliability, initial budget, long-term savings, need for energy independence, available government subsidies, maintenance, and environmental impact of battery use.

